Cervical Herniated Disc Signs and Symptoms
Last Updated on February 8, 2024 by Lily
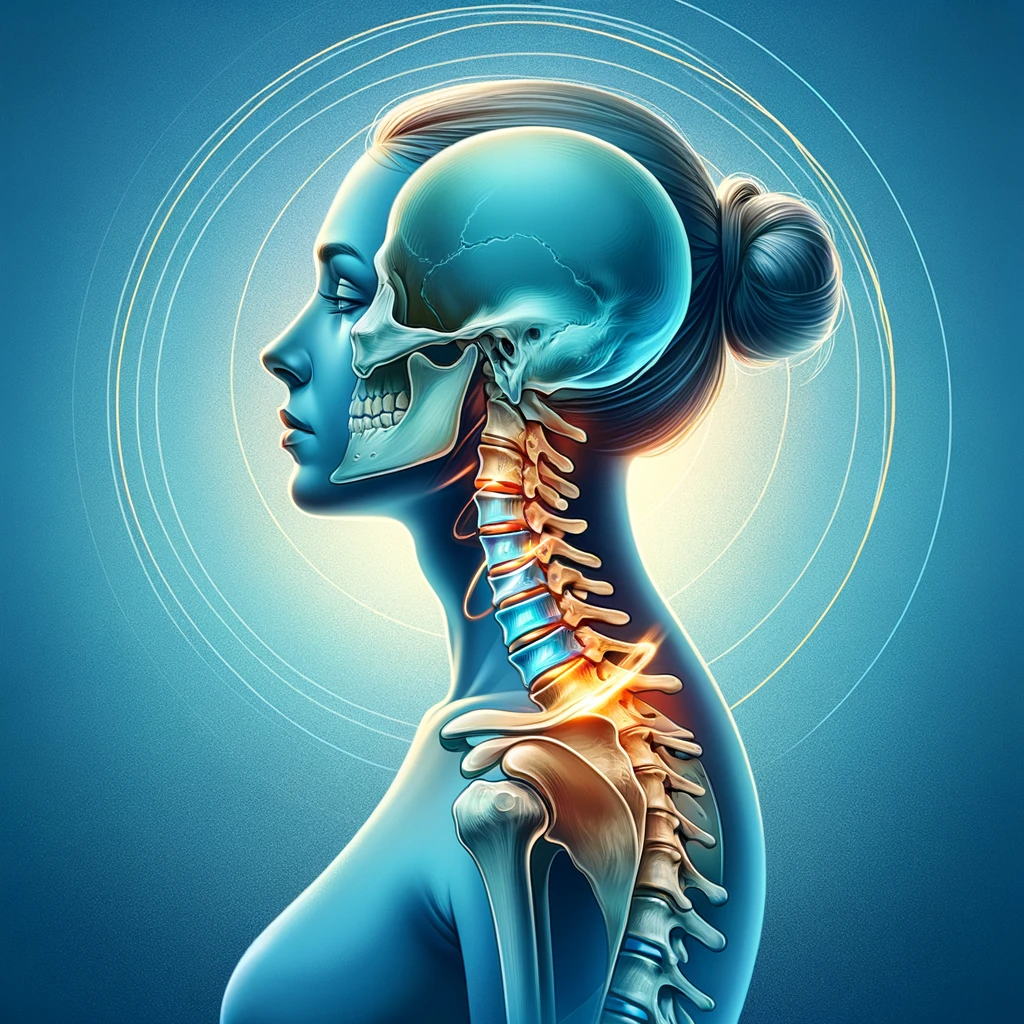
Key Takeaways
1. Neck Pain: Persistent or sharp pain in the neck, often radiating to the shoulder or arm, is a common symptom of a cervical herniated disc.
2. Arm Pain: Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arms or hands, especially on one side of the body, may indicate nerve compression due to a herniated disc.
3. Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the muscles of the arms or hands, particularly when gripping objects or lifting, can be a sign of nerve compression from a herniated disc.
4. Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the neck or experiencing stiffness and discomfort during certain movements may suggest a cervical herniated disc.
Cervical herniated discs occur when the soft, gel-like center of a spinal disc in the neck pushes through a tear in the outer layer, causing pain and discomfort. Understanding the anatomy of the cervical spine and the common causes of disc herniation is essential for recognizing and managing this condition effectively.
Understanding Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of cervical herniated discs is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms may vary depending on the severity and location of the herniation, but common indicators include neck pain, radiating arm pain, muscle weakness, numbness and tingling sensations, limited range of motion, and headaches.
Neck Pain and Discomfort
Neck pain is a primary symptom of cervical herniated discs and is often described as dull or sharp, localized in the neck region. The pain may worsen with certain movements or activities and can significantly impact daily life and function.
Radiating Arm Pain
Radiating arm pain, known as radicular pain, occurs when the herniated disc compresses nearby spinal nerves, causing pain to travel from the neck down the arm. This pain may be sharp, shooting, or burning in nature and may be accompanied by weakness or numbness in the affected arm.
Muscle Weakness and Atrophy
Muscle weakness and atrophy may develop in the muscles supplied by the compressed nerves, leading to decreased strength and function. Commonly affected muscles include those responsible for shoulder and arm movements, resulting in difficulty with tasks such as lifting and gripping objects.
Numbness and Tingling Sensations
Numbness and tingling sensations, also known as paresthesia, may occur in the arms, hands, and fingers due to nerve compression. These sensations may vary in intensity and duration and may be accompanied by a loss of sensation or altered sensation in the affected areas.
Limited Range of Motion
Cervical herniated discs can restrict the normal range of motion in the neck, making it difficult to perform everyday activities such as turning the head or looking up and down. Stiffness and discomfort may be particularly noticeable in the morning or after prolonged periods of inactivity.
Headaches and Associated Symptoms
Headaches may occur as a secondary symptom of cervical herniated discs, particularly if the pain radiates from the neck to the head. These headaches, known as cervicogenic headaches, may be accompanied by additional symptoms such as dizziness, visual disturbances, and nausea.
Exacerbating Factors
Certain activities and positions, such as bending forward, lifting heavy objects, or prolonged sitting, may exacerbate symptoms of cervical herniated discs. Avoiding these aggravating factors and practicing proper ergonomics can help alleviate discomfort and prevent further injury.
Recognizing Signs of Nerve Compression
Severe symptoms indicating nerve compression, such as muscle weakness, loss of coordination, or bowel or bladder dysfunction, require immediate medical attention. These symptoms may indicate a more serious condition, such as cauda equina syndrome, which requires prompt intervention to prevent permanent nerve damage.
Diagnostic Process and Evaluation
Diagnosing cervical herniated discs typically involves a thorough physical examination, medical history review, and diagnostic imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans. These tests help identify the location and severity of the herniation and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Treatment for cervical herniated discs may include conservative approaches such as rest, physical therapy, medications, and epidural steroid injections to alleviate pain and inflammation. In severe cases or when conservative measures fail to provide relief, surgical interventions such as discectomy or spinal fusion may be considered.
Lifestyle Modifications and Preventive Measures
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing good posture, and engaging in regular exercise can help prevent cervical herniated discs and reduce the risk of recurrence. Ergonomic adjustments in the workplace and avoiding activities that strain the neck can also help protect the cervical spine from injury.
Coping Strategies and Support Resources
Living with cervical herniated discs can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, joining support groups, and practicing stress management techniques can help individuals cope with pain and maintain a positive outlook on their recovery journey.
Conclusion
Cervical herniated discs can cause a range of signs and symptoms that vary in severity and impact on daily life. Recognizing these symptoms early and seeking prompt medical attention is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. With appropriate care and management strategies, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.



